World Health Assembly Statement Analysis: Older People, Vaccination
Following the World Health Assembly, held from 18-19 May 2020, the IFA completed an analysis on the statements submitted under agenda item 3, devoted to the COVID-19 pandemic response, regarding two topics: Older People and Vaccination.
Older People
COVID-19 has brought with it many unprecedented challenges, particularly regarding older people and those with underlying conditions such as diabetes, heart disease and respiratory conditions rendering them at a higher risk of contracting the virus. Today more than ever, discrimination against older people has revealed itself in life or death consequences.
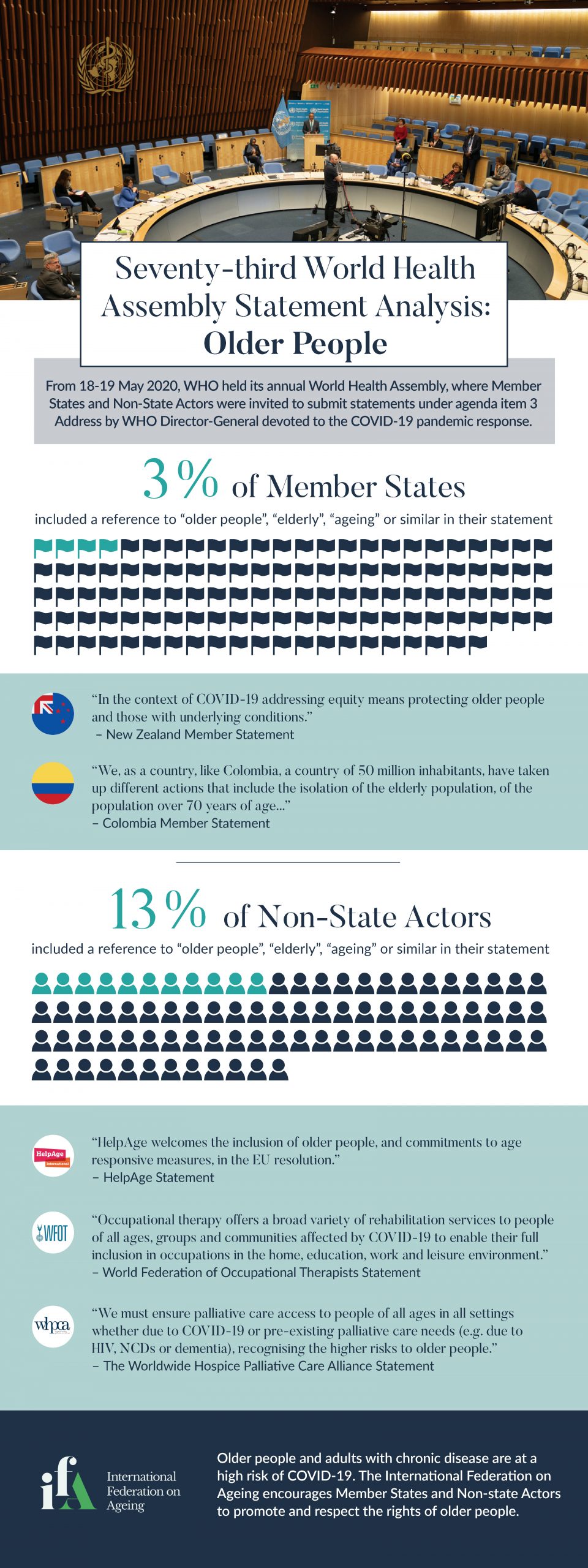
At the World Health Assembly held from 18-19 May 2020, under agenda item 3 devoted to the COVID-19 pandemic response, 3% of Member States and 13% of Non-State Actors mentioned “older people”, “elderly”, “ageing” or similar in their submitted statement, according to an analysis completed by the International Federation on Ageing (IFA).
Aligned with the Decade of Healthy Ageing 2020-2030, the International Federation on Ageing calls on Member States to prioritize the legal rights of older people to live long and healthy lives within the four action areas: ageism, integrated primary care, long term care and age-friendly cities and communities specifically through:
- Addressing the needs of older persons during periods of fiscal consolidation after the pandemic, through investment in age-friendly health systems, community services, and environments;
- Prioritizing the establishment and / or reform of long-term care systems as a priority to current and future generations of older people and their families;
- Improving testing and treatment and ensuring adequate, integrated health care of older persons during and after the COVID-19 pandemic;
- Investing in the collection and utilization of disaggregated data beyond 70 years of age, which is essential to ensuring no one is left behind; and
- Reconfirming the critical role of civil society in intergovernmental deliberations, as both implementers and partners, as is highlighted as a requirement in the Sustainable Development Goals.
Vaccination
COVID-19 is providing a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of infectious diseases in a globally-connected world, and raising questions about the imminent, overwhelming demand for a coronavirus vaccine, as well as the essential need for routine vaccinations against influenza and pneumococcal pneumonia throughout and after the pandemic.
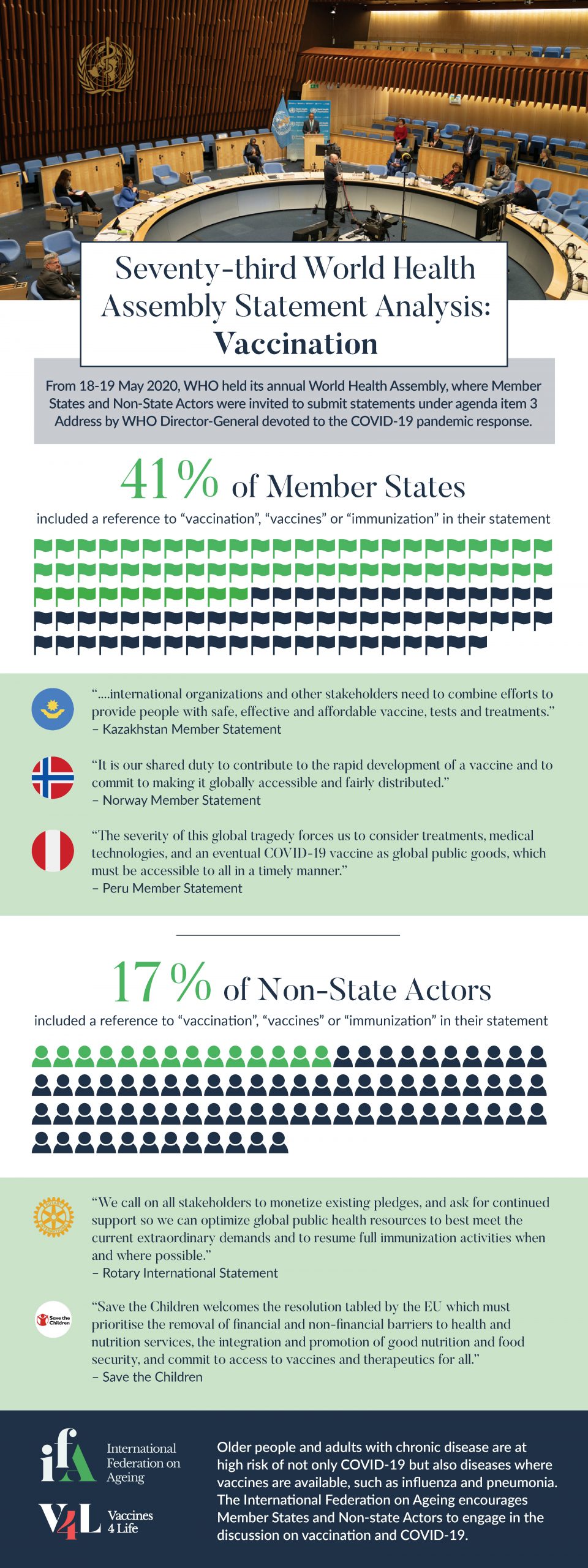
At the World Health Assembly held from 18-19 May 2020, under agenda item 3 devoted to the COVID-19 pandemic response, 41% of Member States and 17% of Non-State Actors included mentioned “vaccines”, “vaccinations” or “immunization” in their submitted statements, according to an analysis completed by the International Federation on Ageing (IFA).
The IFA commends those Member States and Non-State Actors and believes that now is the time to recognise the value of life course vaccination policies on the global scale, and to reverse the recent downward trend in adult vaccination.
Especially considering the exceptional budgetary challenges that will face all countries post-pandemic, advocating against fiscal austerity and for significantly greater investment into preventive interventions is critically important. A re-orientation of global immunization policies for many vaccine preventable diseases must ensure that safe and effective vaccines are available in a manner that leaves no one behind, regardless of age or socioeconomic background.